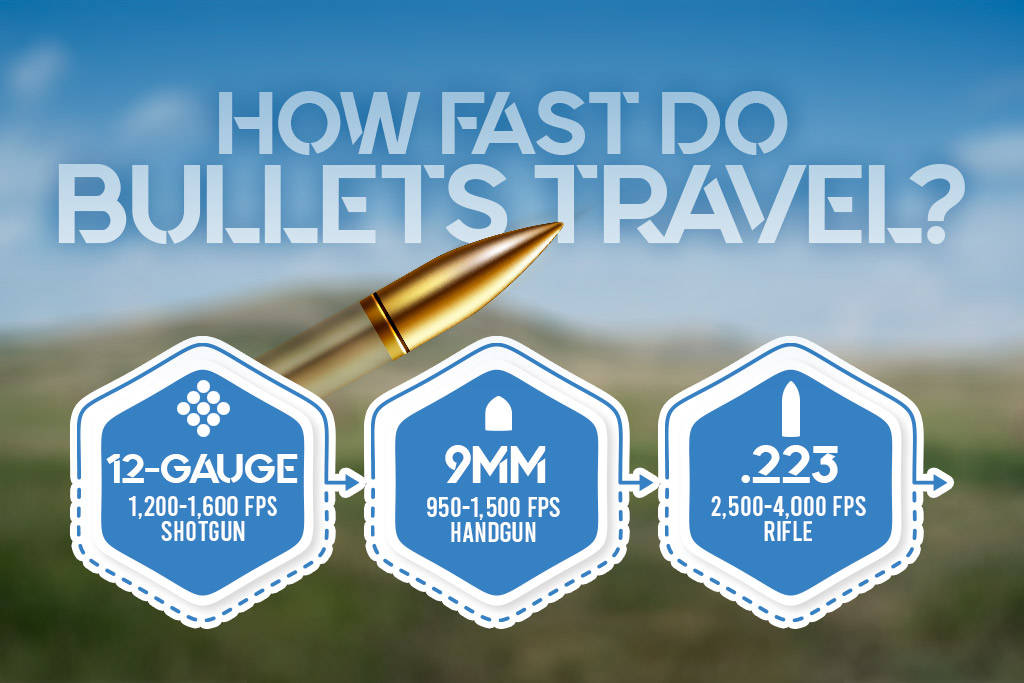
LP in Finance: Understanding Limited Partnerships and Their Investment Implications
What does LP stand for in finance?
In the finance world, LP well-nigh normally stand for limited partnership. This is a specific type of business structure that combine elements of partnerships and corporations, offer unique advantages for certain investment scenarios and business operations.
The fundamentals of limited partnerships
A limited partnership is a business arrangement where two or more parties join forces, but with distinct roles and levels of liability. The structure include:
-
General partners (gGPS)
these individuals or entities manage the partnership’s operations and bear unlimited liability for the partnership’s debts and obligations. -
Limited partners (lLPs)
these are passive investors who contribute capital but have minimal involvement in day to day operations. Their liability is limit to the amount of their investment.
This arrangement create a clear separation between management and investment, make LPs attractive for specific financial scenarios.
Key characteristics of limited partnerships
Liability protection
One of the primary benefits of the LP structure is the liability protection it offers to limited partners. Unlike general partnerships where all partners face unlimited liability, limited partners inan LP risk exclusively their invest capital. This protection make LPs appeal to passive investors who want exposure to certain investments without risk personal assets beyond their initial contribution.
Tax advantages
Limited partnerships offer significant tax benefits that attract many investors:
-
Pass through taxation
lLPsdon’t pay corporate income tax. Rather, profits and losses ” ass done “” the partners, who report them on their individual tax returns. -
Tax efficient income distribution
partners can receive distributions that may be tax at more favorable rates than ordinary income. -
Deductible losses
in some cases, limited partners can use partnership losses to offset income from other sources.
Governance structure
The governance of a lLPfollow a clear hierarchy:
- General partners maintain complete management control and make all operational decisions.
- Limited partners have restrict voting rights, typically exclusively on fundamental issues like dissolve the partnership or remove general partners.
- The partnership agreement define the specific rights, responsibilities, and profit share arrangements between all parties.
Common applications of limited partnerships
Private equity and venture capital
The LP structure dominate the private equity and venture capital industries. In these arrangements:
- Investment management firms serve as general partners, contribute a small percentage of capital (typically 1 2 % )but receive management fees and carry interest.
- Institutional investors and high net worth individuals act as limited partners, provide the majority of investment capital.
- This structure align incentives, as general partners earn significant returns exclusively if they generate profits for the limited partners.
For example, a typical private equity fund might raise $500 million from pension funds, endowments, and wealthy individuals ((s lpLPs)with the private equity firm contribute $ 1$10llion as the gp wGPle manage all investment decisions.
Real estate investments
Real estate developers and investors often use limited partnerships to structure property investments because:
- They allow developers (as gGPS)to maintain control over property management and development decisions.
- Passive investors (as lLPs)can participate in real estate opportunities without management responsibilities.
- The pass through tax treatment permit efficient handling of depreciation deductions and other real estate tax benefits.
Many real estate investment trusts (rrats))nd real estate funds utilize lp LPructures or variations like limited liability limited partnerships ( l(phelps)
Energy and natural resources
The energy sector, peculiarly oil and gas exploration, usually employ limited partnerships:

Source: bbcincorp.com
- Master limited partnerships (mmaps)are publically trade lpLPshat combine limited liability with liquidity.
- These structures are popular for pipeline operations, oil and gas drilling programs, and mineral rights investments.
- Energy maps oftentimes distribute significant income to investors while offer tax advantages through depletion allowances and other industry specific benefits.
Limited partnerships vs. Other business structures
LP vs. General partnership
Unlike general partnerships where all partners have management rights and unlimited liability, LPs create a two tier system:
- General partners in a lLPbear unlimited liability and control operations.
- Limited partners enjoy liability protection but surrender management control.
- This distinction make LPs more suitable for passive investment arrangements.
LP vs. LLC (limited liability company )
While both structures offer liability protection, they differ in several key aspects:
- LCS provide liability protection to all members, not exactly a specific class of investors.
- LCS offer more flexibility in management structure and profit distribution.
- LPs maintain a clearer distinction between management and investment roles.
- LPs are oftentimes preferred for investment funds due to their established legal precedents and investor familiarity.
LP vs. Corporation
Limited partnerships differ importantly from corporations:
- Corporations face double taxation (corporate and shareholder levels ) while lpLPsffer pass through taxation.
- Corporations have perpetual existence, while LPs typically have defined lifespans.
- Corporate shareholders have no direct liability, similar to limited partners, but different from general partners in a lLP
- Corporations have more complex governance requirements, include boards of directors and shareholder meetings.
Legal formation and requirements
Establish a limited partnership
Create a limited partnership involve several critical steps:
- File a certificate of limited partnership with the appropriate state authority
- Draft a comprehensive limited partnership agreement
- Secure any necessary business licenses or permits
- Establish a registered agent and office in the state of formation
- Create operating procedures that maintain the distinction between general and limited partners
Partnership agreement essentials
An intimately structure limited partnership agreement should address:
- Capital contributions and commitment periods
- Profit and loss allocation formulas
- Distribution policies and priorities
- Management rights and restrictions
- Transfer restrictions on partnership interests
- Dissolution triggers and procedures
- Reporting requirements and partner communication protocols
Regulatory considerations
Limited partnerships face various regulatory requirements depend on their activities:
- Investment focus LPs may need to comply with securities regulations, include private placement rules.
- Publically trade LPs must meet exchange listing requirements and sec report obligations.
- Industry specific regulations may apply to LPs in sectors like energy, real estate, or financial services.
- Tax reporting requirements include file annual partnership returns and issue schedule k 1s to partners.
Advantages and disadvantages for investors
Benefits of investing as a limited partner
Limited partners enjoy several advantages:
- Access to investment opportunities that might differently be unavailable to individual investors
- Professional management by experienced general partners
- Liability protection that cap risk at the investment amount
- Tax efficient structure for certain types of investments
- Potential for higher returns in specialized investment areas
Drawbacks and risks
Notwithstanding, LP investments come with notable drawbacks:
- Limited control over investment decisions and operations
- Typically, longer investment horizons with limited liquidity
- Reliance on general partners’ expertise and integrity
- Complex tax reporting requirements
- Potential conflicts of interest between general and limited partners
Suitability for different investor types
Limited partnership investments are broadly virtually appropriate for:
- Accredited investors with substantial net worth or income
- Institutional investors seek portfolio diversification
- Investors with long term investment horizons
- Those seek tax advantaged investment structures
- Investors comfortable with reduced liquidity and control
Other meanings of LP in finance
While limited partnership is the well-nigh common meaning of LP in finance, the abbreviation can have other meanings in specific contexts:
-
Liquidity provider
in trading markets, lLPsare entities that quote both buy and sell prices, provide market liquidity. -
Loan participation
in banking, lLPcan refer to an arrangement where multiple lenders fund portions of a single loan. -
Liquidity premium
in investment theory, lLPrepresent the additional return investors demand for hold less liquid assets. -
Limited payment
in insurance, lLPpolicies have premium payments for a specify period instead than the full policy term.
Current trends in limited partnerships
Evolution in private markets
The limited partnership model continues to evolve in private markets:
- Longer term funds extend beyond the traditional 10-year lifecycle
- Hybrid structures combine elements of LPs with other investment vehicles
- Increase transparency and reporting to limited partners
- More customize fee arrangements and alignment mechanisms
Regulatory changes
Regulatory developments affect limited partnerships include:

Source: wholesaleinvestor.com
- Enhance disclosure requirements for private fund managers
- Greater scrutiny of tax benefits associate with carry interest
- Evolving standards for qualifying as accredited investors
- International tax harmonization efforts impact cross border LP structures
Conclusion
The LP structure remain a cornerstone of modern investment frameworks, peculiarly in alternative assets. Understand what LP stand for in finance — limited partnership — provide insight into a versatile business structure that balance management control, investor protection, and tax efficiency. For investors and financial professionals likewise, recognize the implications of the LP designation help navigate investment opportunities across private equity, real estate, energy, and other sectors where this structure predominate.
Whether consider an investment as a limited partner or structure a business as a limited partnership, the distinct roles, responsibilities, and protections inherent in the LP model continue to make it a valuable component of the financial landscape.
MORE FROM getscholarships.net